Earth-observation data is evolving fast, and so is the need for tools that help us push its limits. Today we’re excited to introduce OpenSR-SRGAN, our new open-source framework designed to make GAN-based super-resolution practical, reproducible, and easy to experiment with across a wide range of satellite sensors and spectral bands.
OpenSR-SRGAN is now publicly available and published as a software package (DOI included in the paper). It’s part of the growing OpenSR ecosystem developed at the Image & Signal Processing Group (IPL), University of Valencia, funded by the OpenSR project by ESA’s Φ-Lab.
🚀 Why We Built OpenSR-SRGAN
GANs remain incredibly powerful tools for generating high-frequency detail, but anyone who has trained them knows the pain: instability, weird dynamics between generator and discriminator, sensitivity to hyperparameters… and that’s before dealing with multispectral inputs.
OpenSR-SRGAN solves these pain points by offering:
A unified, modular architecture for generators & discriminators
Config-driven experimentation via simple YAML files
Native support for arbitrary spectral bands (RGB, NIR, SWIR, and beyond)
Training stabilization mechanisms built-in (warmup, label smoothing, EMA, etc.)
Seamless integration with the rest of the OpenSR ecosystem: SEN2NAIP dataset, opensr-test, and opensr-utils
Instead of modifying code for every new experiment or sensor, users only edit a configuration file. This keeps the workflow clean, reproducible, and beginner-friendly.
All of this is described in detail in the software paper (see pages 1–3 for the motivation and contributions)
🧠 What’s Inside the Framework?
1. Interchangeable Generators
You can switch between several backbone styles (SRResNet, RCAB, RRDB, ESRGAN, large-kernel attention, even a conditional/noise-augmented cGAN generator) simply by editing a flag in your config.
Appendix A (page 8) lists all generator types and their characteristics.
2. Multiple Discriminator Options
Depending on your goal, pick:
a global SRGAN discriminator,
a PatchGAN, or
a deep ESRGAN-style discriminator.
See Table 2 on page 8 for a quick comparison.
3. Built-In Training Stabilization
Out of the box, the framework includes:
generator pretraining,
adversarial ramp-up,
warmup schedules,
label smoothing,
TTUR,
Exponential Moving Average (EMA) of weights (Section 4.3 & 4.3.2).
These features make training far less chaotic than standard GAN implementations.
4. A Config-First Workflow
Everything—architecture, dataset, losses, optimizers, training schedules—is controlled from a YAML file.
You don’t touch model code unless you want to.
🌍 Designed for the EO Community
OpenSR-SRGAN is not meant to be “the best SR model ever.”
Instead, it’s designed to be:
a reliable baseline,
a testbed for new ideas,
a reproducible benchmark, and
a practical tool for multispectral and multisensor workflows.
It offers a clean engineering foundation so researchers can focus on ideas, not boilerplate.
📦 Get Started
The source code and ready-to-run examples are available at:
👉 https://github.com/ESAOpenSR/SRGAN
If you’re already using other OpenSR tools like opensr-test or opensr-utils, this package slots right in.
📊 Examples From the Paper
The paper includes two reference experiments demonstrating how the framework handles both RGB super-resolution and multispectral/SWIR reconstruction.
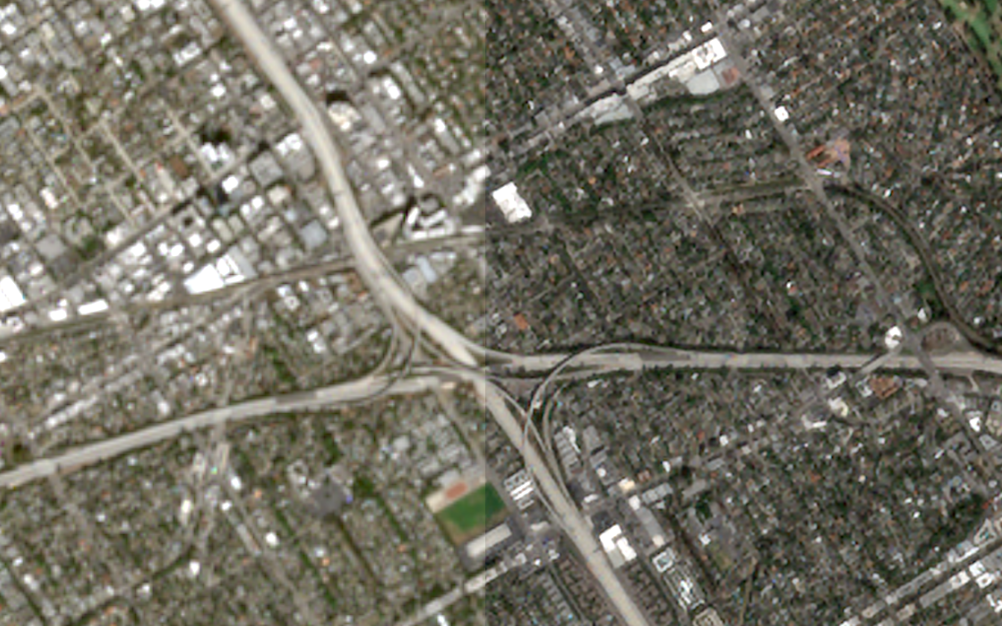
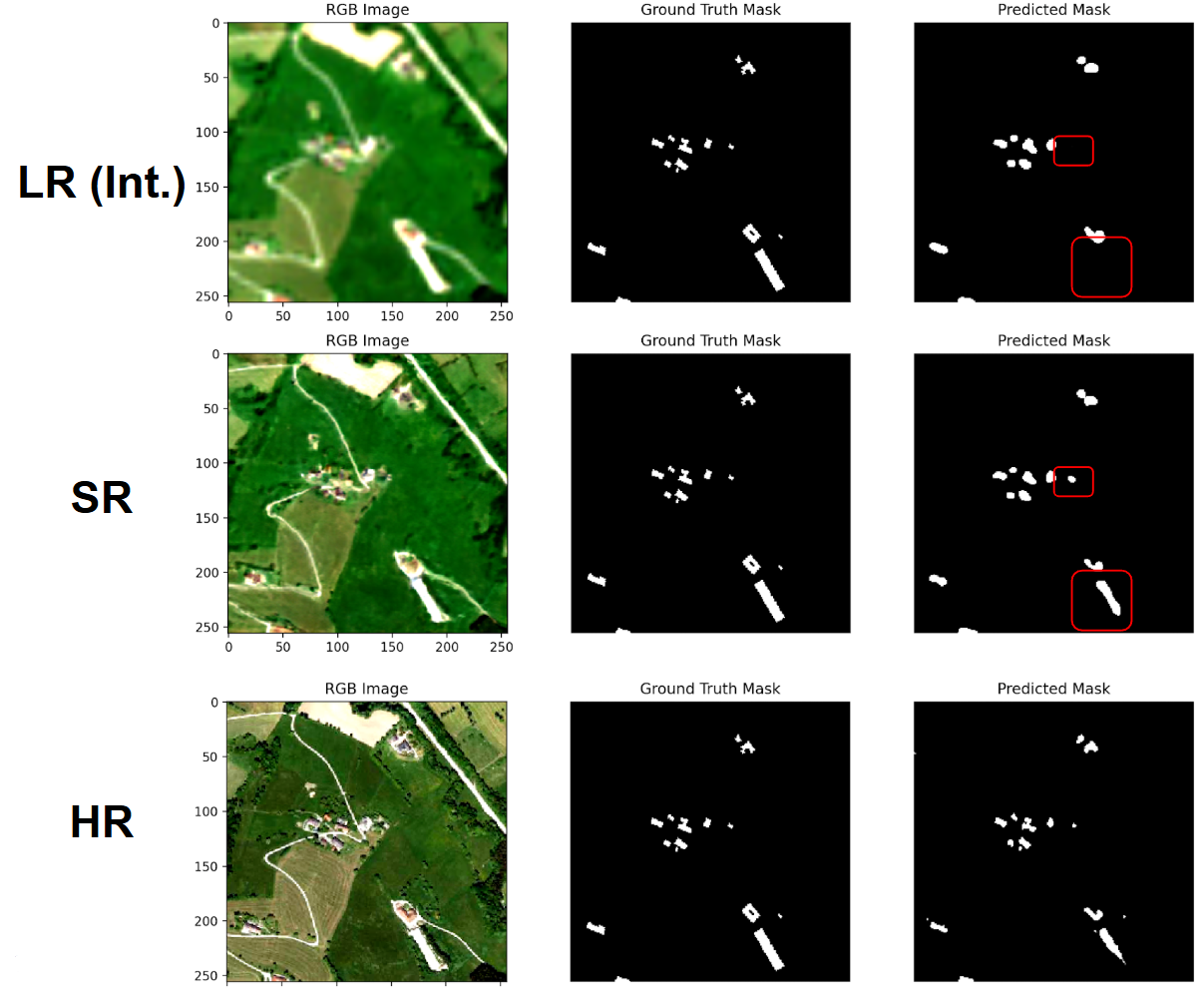
Example 1 — 4× RGB-NIR Super-Resolution (SEN2NAIP)
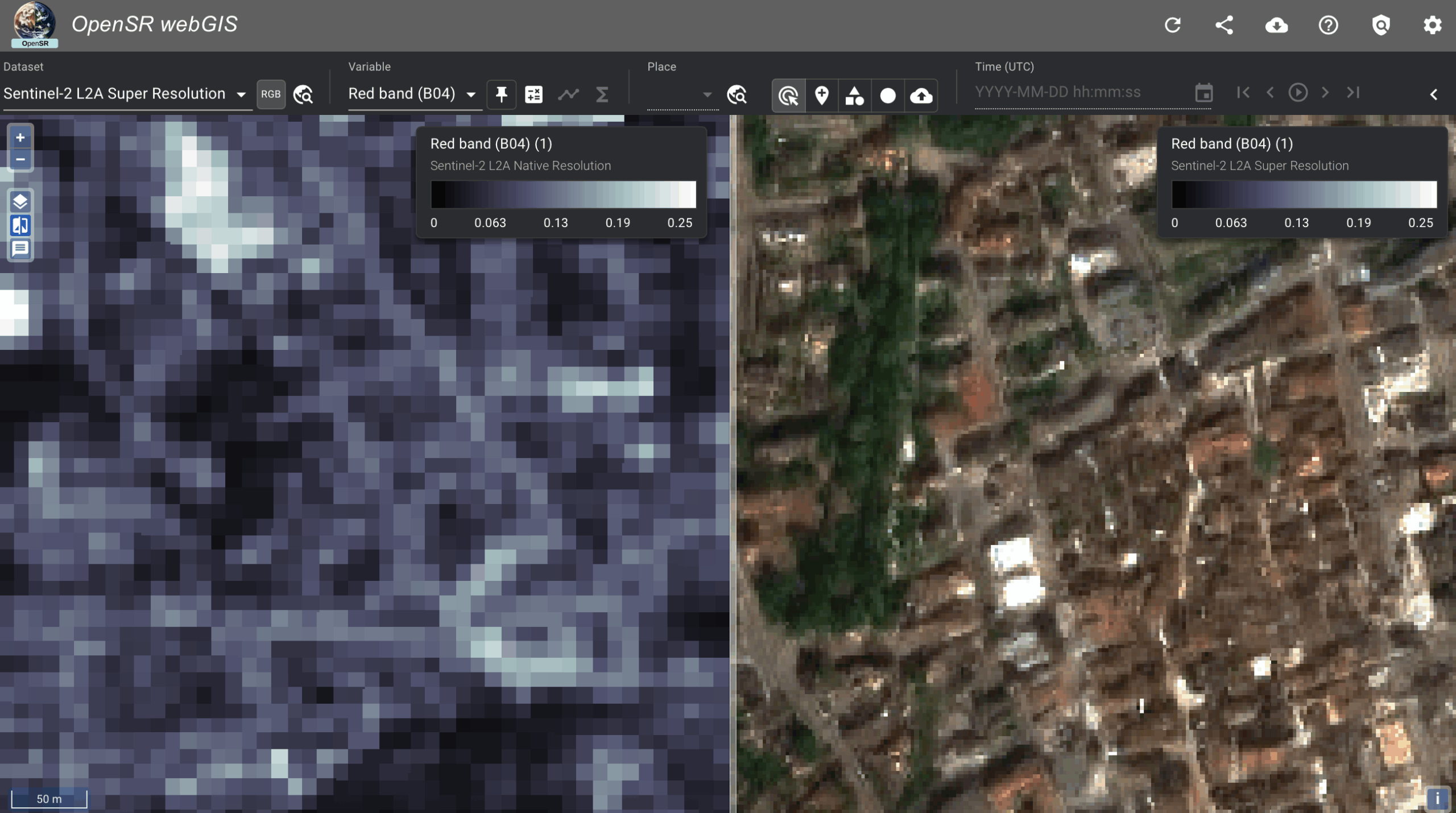
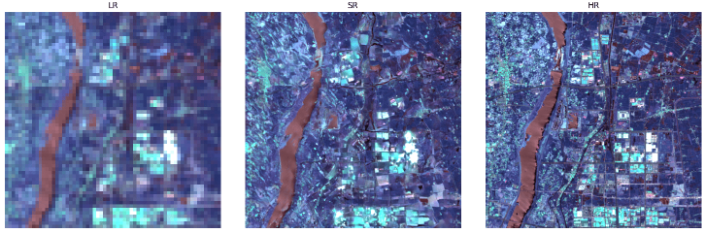
As shown in Figure 2 on page 10, the framework enhances Sentinel-2 RGB/NIR from 10m to 2.5m, producing noticeably sharper buildings, field boundaries, and road structures.
The setup uses an RCAB-based generator and an SRGAN discriminator, trained with L1 + perceptual + adversarial loss.

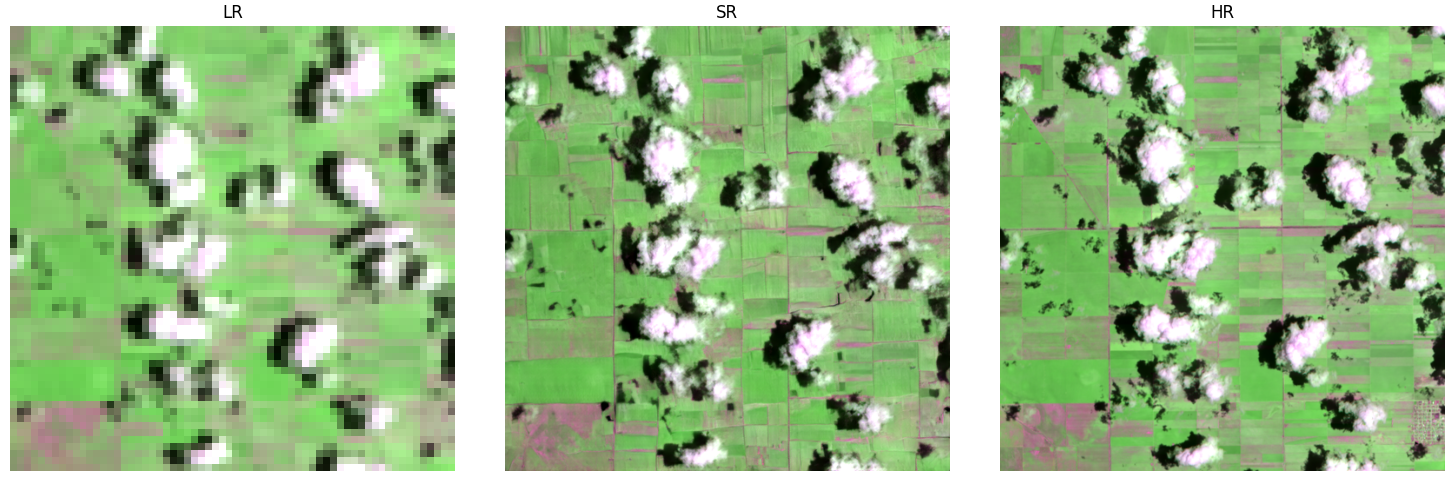
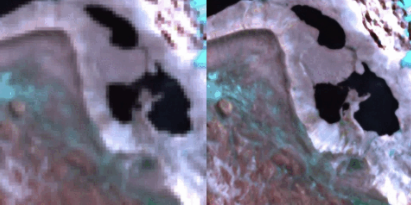
Example 2 — 8× Multispectral SWIR Super-Resolution
Shown in Figure 3 on page 12, OpenSR-SRGAN successfully reconstructs 20m Sentinel-2 bands from synthetically degraded 160m inputs, recovering edges and small structures while preserving band-wise spectral consistency.
This experiment uses a PatchGAN discriminator with emphasis on L1 + SAM losses.
The tables on pages 11–12 summarize configurations, PSNR/SSIM/SAM results, and model performance.
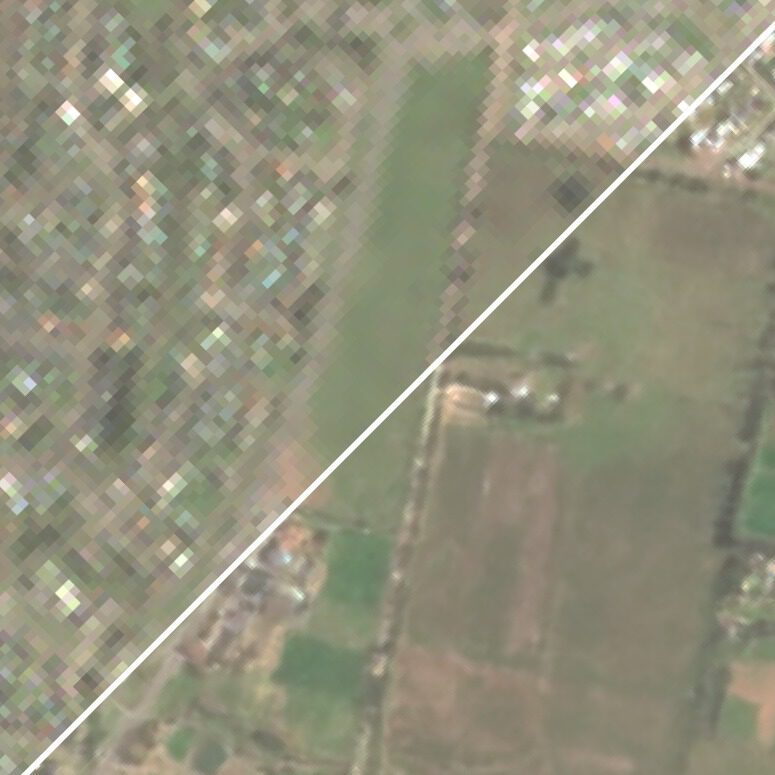
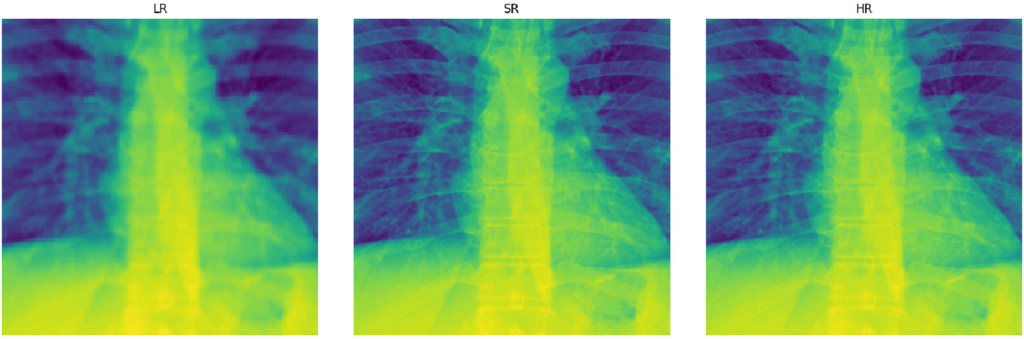
Example 4 — 4× Single-Channel Medical Image SR Example
Just as an experiment, we test how well the general framework si able to generalize to other domains. Just based on standard image metrics, it seems like SRGAN is able to produce competitive results. Importantly, the modular design allows the user to immediately start experimenting with their own data, normalizations and architectures.